Custom VPN vs Open Source VPN – A Full Walkthrough
A Custom VPN vs Open Source VPN comparison? The adoption of virtual private networks (VPNs) is growing, and it’s growing fast. In fact, the global VPN market is expected to reach USD 71.33 Billion by 2027. Nowadays, organizations are looking to secure their online communications. They’re also trying to prevent hackers and governments from snooping on their data traveling the Internet.

Users will come across two types of VPNs – Custom VPNs and Open Source ones. Open-source VPNs are well-known for their transparency and flexibility. However, custom ones are easy-to-use and are made for any internet user regardless of his/her technical knowledge. So, the question is: How do these two compare? Are Open-source VPNs better and safer than custom ones? It all depends on the user’s level of technical know-how, which is what you’ll be getting in this Custom VPN vs Open Source VPN guide.
Virtual Private Networks – The Custom/Open-Source Dilemma
A reliable VPN is exactly what its name suggests: A ‘private’ tunnel for establishing communication between two end-points such as two or more computers, mobile devices, or entire networks.
While there are a number of trusted service providers on the market for enterprise-grade VPN services, you face a certain problem related to the nature of closed-source code VPN apps.
You cannot inspect the programming code of a VPN software unless it is open-source. Otherwise, you entrust the VPN vendor not to include backdoors or tracking code into their VPN app.
Thus, you have basically two options when it comes to deciding about adopting a VPN solution you trust – you trust the VPN provider or you trust the source code.
In fact, you can have both a closed-source and open-source VPN that is customizable but let’s focus on adopting a custom open-source VPN, which offers both advanced customization and transparent source code.
Developing a proprietary custom VPN app works for very large organizations only, so we will not review this option here.
Custom VPN vs Open Source VPN – What is Custom OpenVPN Connection
Currently, the industry to a very narrow choice of highly secure network protocols that are with open source. And the best VPN protocol that is open-source goes under the name OpenVPN.
While you are limited to OpenVPN in this case, the good news is that generic OpenVPN clients are available for any major operating systems – Windows XP and up to Windows 10, macOS, and Linux – as well as for Android and iOS mobile operating systems.
Most of the popular VPN solutions provide support for the OpenVPN protocol and standard configurations enable you to connect via OpenVPN even if the OpenVPN software is not available for your specific OS. It sounds weird but it works.
These capabilities enable you to set up and configure a custom VPN connection that is also open source. In addition, you can have an OpenVPN installed on your routers by adding open source DD-WRT or Tomato router firmware. These add-ons extend your router’s capabilities, including the option for installing a VPN solution based on OpenVPN.
A drawback of such a solution is that you need to download the configuration files for your OpenVPN client from the respective VPN provider in order for the system to work.
The entire process is a bit more complicated compared to using a generic OpenVPN client. But in the end, it pays off since you will be customizing a VPN service to your needs.
Alternative open-source VPN solutions for creating your own VPN are also available. You should be aware, however, that some of them are harder to configure and set up when compared to stock open-source OpenVPN clients.
Building Custom VPN outside OpenVPN
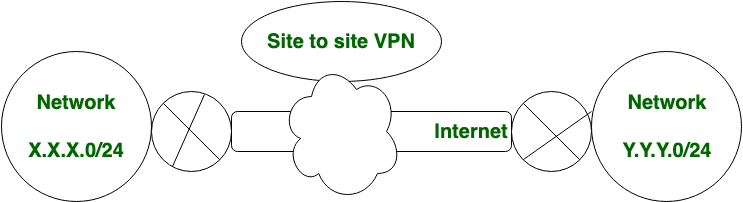
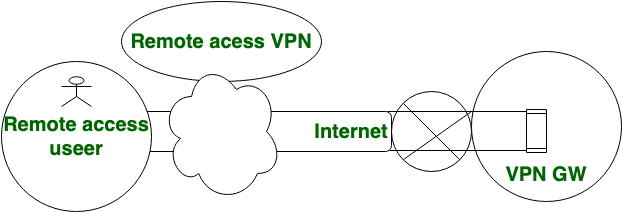
Organizations usually implement VPN solutions for two reasons. First, to enable secure connections between remote offices via a public network like the Internet. Second, to allow employees to connect to a corporate network from remote locations outside the company offices. We call the former VPN solution “site-to-site VPN” and the latter “remote access VPN.”
A visual representation of both types can be seen in the images below:
- Here’s how site-to-site VPNs work:
- Now, this is how remote access VPNs operate:
In this respect, any corporate VPN connection represents a custom VPN as it connects unique locations and enables unique users to use the service while every corporate VPN is set up to service your specific needs.
Nonetheless, many business users turn to open-source VPNs to get more customization options. Below we are listing a number of open-source VPNs that allow for a hybrid approach by enabling you to use a combination of network protocols for better security and cost-efficiency.
SoftEther
(Software Ethernet) supports network protocols such as SL VPN, L2TP/IPSec, OpenVPN, and Microsoft SSTP and offers high data throughput and low latency while demonstrating high resistance to firewalls. It is one of the more popular alternatives to both closed-source VPNs and OpenVPN clients.
Algo VPN
It is a solution that creates an on-demand VPN service in the cloud after you set up a self-hosted IPSec VPN. The cloud-based VPN service is not shared with other users but only support for IKEv2 connections with encryption algorithms is available.
Streisand
This one works in a similar fashion to Algo but is available only for Ubuntu 16.04 server. It supports L2TP, OpenConnect, OpenSSH, OpenVPN, Shadowsocks, Stunnel, Tor Bridge, and WireGuard, thus offering a wider choice of connectivity options.
PriTunl
Pritunl is another cloud-based VPN that offers data encryption, complex site-to-site links, and gateway links. The VPN service supports remote access via a Web-based interface for users within a local network.
strongSwan
strongSwan is an open-source multi-platform IPSec solution that works on Linux, Windows, macOS X, FreeBSD, and Blackberry OS. The VPN uses IKEv1 and IKEv2 key exchange protocols and implements UDP encapsulation and port floating for NAT-traversal. VPN clients get their virtual IP addresses automatically while they implement encryption through modular plugins.
WireGuard
Next, there’s WireGuard. It is an easy-to-configure VPN solution that performs better than most of the other open-source VPNs. It takes care of most of the VPN settings automatically as it is intended to work as a general-purpose VPN but with faster data transfer speeds and high-grade encryption.
FreeLan
Finally, we have FreeLan. A VPN solution in which you have no graphic user interface (GUI). However, it can create client-server, peer-to-peer, and hybrid network solutions for secure VPN connections.
You can create a reliable VPN configuration using any of the above open-source VPNs if you have at least basic computer networking knowledge required to configure the respective VPN for best performance and security.
Custom VPN vs Open Source VPN – Concluding Words
Custom-made VPNs add further layers of privacy and security to your online communications. However, they need to be properly set up and configured to deliver results. With open-source VPN solutions, you can even inspect the source code of the application to make sure it does not snoop on you. But keep in mind that doing this requires even more advanced IT and computer programming skills.
What it means is that a customizable open-source VPN is not for everyone. If you need a VPN to bypass geo-blocking restrictions, stay with a stock VPN client be it closed-source or open-source.
Opt for a highly customizable and open-source VPN only if you need a secure custom connection for business use e.g. for connecting your remote offices or enabling employees to work from home or on the field.
Did this guide give you all you’re looking for? Share you thoughts and comments below.





