What is VPN Obfuscation and How Does It Protect You?
As the use of virtual private networks (VPNs) is increasing, so is growing the use of tools to detect VPN traffic by governments, online service providers, and hackers. The main goal of using a VPN at home or at work is to have better privacy and security online. When governments are trying to detect VPN traffic, their goal is to know who is accessing what. Online service providers have other reasons to detect VPNs, mostly related to copyrights.

Masking your Internet traffic as if it’s not passing through a VPN has several names. We can call it “VPN obfuscation”, “traffic obfuscation” or “stealth VPN”. These are all one and the same thing; namely, a method and technology to hide the very fact you are using a VPN, masking your traffic as ‘ordinary’ Internet traffic.
How does VPN Obfuscation work?
Any protocol you use to connect to the Internet and exchange data over the network has its distinctive signature that a third party can detect and recognize when analyzing your data packets. OpenVPN is by far the most VPN protocol and it has its own digital signature as well.
Thus, a third-party snooping on your connection or your Internet service provider (ISP) is able to discover when you are using VPN by utilizing detection methods such as deep packet inspection.
What VPN obfuscation is doing is to make those using such methods believe that you are transferring ‘normal’ data packets while the VPN service in fact still transmits encrypted data packets to secure your communications.
VPN applications use different methods to mask your traffic but the general idea is to add a layer of encryption that makes your encrypted traffic look like regular traffic. Even a free and widely available tool for network traffic inspection can detect the use of a VPN.
Digging a Bit Deeper!
Take a look at the screenshot below, where a ‘normal’ VPN connection is being inspected.
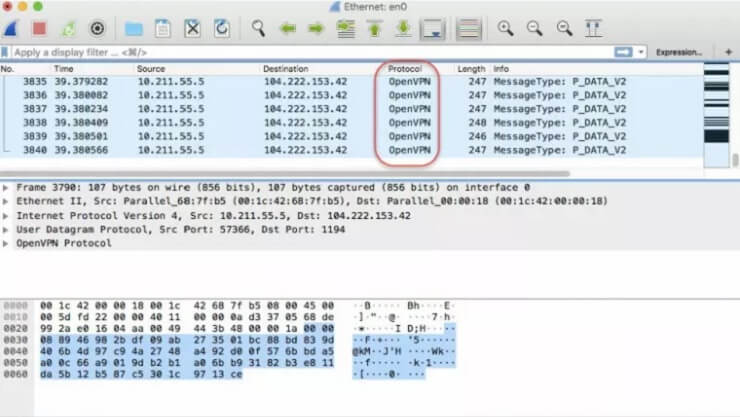
You can see that the traffic monitoring software detects and notifies that the connection being scrutinized is using OpenVPN as communication protocol, making it clear to the observer that the source and the destination connect over a VPN.
It does not mean that your encryption is being broken and someone can read the data you exchange. It means that this person knows you are using a VPN agent to connect to a VPN server and then reach your destination.
VPN obfuscation actually works by replacing the usual header of OpenVPN packets – which reveal your connection is using a VPN – with data packet headers identifying your traffic as regular.
In fact, this is another layer of encryption but at the top level and it simply makes your traffic look like any other HTTPS traffic, which makes for 90% of all traffic over the Internet.
After obfuscation, the network traffic analyzer will detect the following characteristics of the same connection under scrutiny.
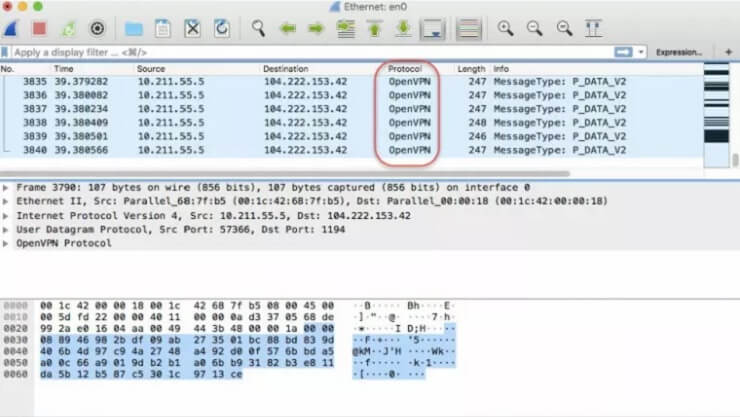
In this case, the VPN obfuscation works by masking your traffic as traffic going through the UDP protocol, which is a common protocol for applications that need require high performance like online gaming or video streaming.
VPN Obfuscation Methods and Tools
Software developers use a number of methods to obfuscate VPN traffic but there is not a broad agreement on which one is the best. Below is a list of the most widely used obfuscation technologies.
- Obfsproxy
Obfsproxy is a method to obfuscate network traffic in the Tor network but it works also with the OpenVPN protocol. Developers use Obfsproxy to run pluggable transports, which scramble the VPN (or Tor) traffic while in the latest version of these transports your traffic looks like virtually nothing.
- Stunnel
What the Stunnel method does is to route your VPN traffic through a TLS/SSL tunnel, which in turn makes the traffic look like any other HTTPS traffic. This is possible because HTTPS is using TLS/SSL to encrypt data and thus a third party will not detect the presence of a VPN.
- OpenVPN XOR Scramble
This method uses the XOR cipher to make OpenVPN traffic undetectable by replacing the value of each bit of data with another value. As a result, data-packet inspection tools cannot detect the OpenVPN pattern in your traffic. It is a controversial VPN obfuscation method, though, as hackers use it to make their code run undetectable.
The technology behind all these VPN obfuscation methods is actually more complex. But for the average user, it is more important to know how obfuscation of VPN traffic enhances his or her online privacy.
How VPN Obfuscation Protects You?
Evidently, VPN obfuscation protects you by pretending your VPN traffic is part of the usual noise HTTPS connections generate. Why then should you hide you are using a VPN? There are at least three reasons for a person to hide his use of a VPN application.
First, there are governments like China or Saudi Arabia that detect VPN traffic and ban the use of (some) VPN services on their territory. Many more governments do not restrict VPN usage but are eager to know who is using VPNs on their territory.
Second, there are service providers such as video streaming companies and online casinos that detect and ban VPN traffic, as they need to keep their licenses to operate in a certain country or region and thus restrict access from these locations.
And then, you have bad actors looking to exploit vulnerabilities in certain VPN apps or searching for users who use a VPN to make financial transactions or procure supplies online.
In any case, obfuscating your VPN traffic as a regular data packets exchange adds a further layer of protection for any user.
What Are the top VPNs with Obfuscation?
This is the hard part for most internet users as they’re unaware which VPNs offer such a feature. As we mentioned, Obfuscation can come in several forms.
Users who are new to this won’t be able to differentiate. Each VPN calls it differently and we’re here to shed more light on the matter.
Now, here are the top VPNs with Obfuscation technology:
- ExpressVPN: The provider is one of the most popular services in the industry. It has a reputation of being able to bypass the Great Firewall of China. How does it do that? It’s simple, obfuscation.
- NordVPN: This one is a bit more clear about their obfuscated servers. There’s a dedicated list that helps you choose the one you want. It is also a great candidate for those living in China, and want to access the internet freely.
- SurfShark: This provider has proved itself worthy to be at the top of the industry. It’s fast, secure, and offers a feature called NoBorders mode that obfuscates your VPN traffic once you activate it.
- PrivateVPN: This provider is fast and reliable. However, if you’re looking for obfuscated servers, you can use their “Stealth VPN” feature. Once you enable it, nothing can detect that you’re using a Virtual Private Network.
- Hotspot Shield: Another great VPN that is able to circumvent detection techniques in highly censored countries. It uses the “Catapult Hydra” protocol to transport your traffic securely and discreetly.
- VyprVPN: The provider is another one that offers obfuscated servers. In fact, most users know VyprVPN for its Chameleon protocol, which helps avoid detection.
Concluding Words
What you need to take into account is that in some highly censored countries, VPN obfuscation can result in more severe fines or legal action compared to the use of ‘normal’ VPNs.
If you are in a place where the use of a VPN is legal, you can try OpenVPN XOR Scramble to unblock a restricted service or access a website that has geo-blocking limitations. Most geo-blocking services will allow VPN traffic passing through OpenVPN XOR Scramble.
Obfsproxy and Stunnel, for their part, enable you to avoid the detection of VPN traffic. This goes specifically when it comes to advanced monitoring tools such as those used by governments. With these tools, you should carefully weigh the pros and cons of using VPN obfuscation in certain locations.
A VPN doesn’t only change your location and encrypt your data. There are a lot of things that happen in the background and now you know one of them. If you have any more questions, drop them in the comments below.





