Introducing ZTNA – Virtual Private Networks Begone?
With so many online threats targetting companies around the world, many organizations resorted to the Zero Trust concept as a strategic approach to cybersecurity that protects their assets and private information. Now, as technology evolved, Zero Trust went from concept/principle to technology with Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).

While there are many ways to enhance a network’s security, ZTNA kicks it up a notch by providing secure remote access to applications and services based on defined access control policies.
In today’s cybersecurity world, there’s one philosophy we have to follow: Noone outside or inside the premises network is to be trusted – anyone can be compromised. ZTNA filters who gets to access what, in the best secure matter. So, what is ZTNA? How secure is it? And does it pose as a good VPN alternative? Find out below.
Zero Trust Network Access – Deep Analysis
During and after the pandemic, 39% of workers use their personal devices to access corporate information. This still remains till today as, in most countries, companies are still allowing their employees to work remotely.
Now, if a single device got compromised, any threat actor may be able to enter the network and cause a major breach. As a result, companies around the world started implementing extra security measures to shield their data.
When it comes to protecting an organization’s assets, ZTNA might be the best option as it secures them from both outside and inside attacks.
The technology uses high-level encryption and other security measures to protect data (sent and received). With such encryption in place, it becomes much more difficult for attacks to intercept the transit and steal sensitive information.
With ZTNA, access is established after the user has been authenticated to the ZTNA service. The ZTNA service then provisions access to the application on the user’s behalf through a secure, encrypted tunnel.
This provides an added layer of protection for corporate applications and services by shielding otherwise publicly visible IP addresses.
The Process
The technology works on an individual scale. What does that mean? Well, instead of securing the entire network as a VPN does, ZTNA leverages the concept of a dark cloud.
Initially, ZTNA doesn’t allow any users to see the company’s apps and services. If they need access, they’ll have to get permission first.
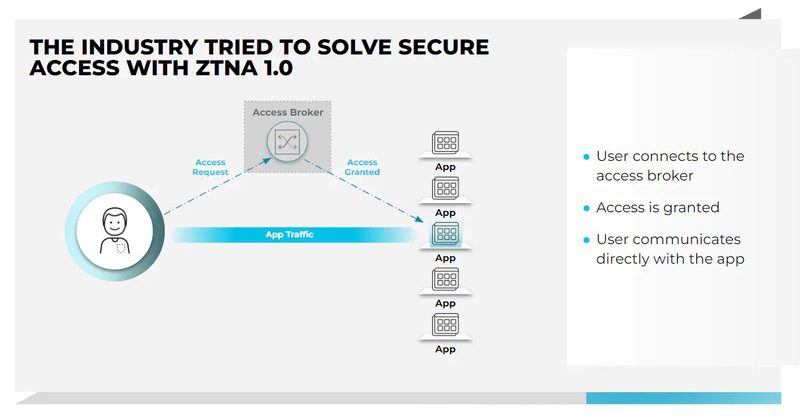
When the users requests access, ZTNA collects the necessary data to identify the user. That includes network details, operating systems, device model, and more.
The data will head straight to the access broker where everything is checked. Once it determines that everything is green-lit, ZTNA creates a secure tunnel from the user’s device to the requested application, nothing more.
Other security implementations might be able to do that. However, the difference here is that ZTNA doesn’t just stop there. In fact, the technology constantly evaluates the security for the remainder of the session.
It takes multiple factors into consideration to see if anything is out of the ordinary:
- Whether the user has changed location.
- When the user last accessed the application.
- If the user is operating on a new device.
- When the actions are abnormal such as altering or deleting data.
If any of these is in place, a whole new verification process initiates and access needs to be permitted once more.
The time needed to access any of the desired apps is quite short. When using a low-latency network such as 5G, the verification process can be completed in a quick manner that might be imperceptible to the end-user.
ZTNA – A VPN Alternative?
This is a tough question actually, but we can answer it regardless. While both might end up doing the same task (Securing an organization’s data), the two technologies couldn’t be any different.
Virtual Private Networks don’t address network security as deeply as zero-trust network access (ZTNA). It mostly relies on broad network-based protection.
A VPN leverages the network layer in order to create a secure connection. On the other hand, ZTNA leverages the application layer to make that connection.
In the security department, we can give ZTNA a soft win since it treats anyone as a potential hacker. VPNs can still be susceptible to outside breaches such as man-in-the-middle attacks and DNS poisoning.
Moreover, a VPN connection can tamper with the user’s connection speed as it takes more time to reroute the data from the user’s location to the server’s physical whereabouts.
Not to mention the load that can be present on the connected server. In other words, operating a VPN might result in high latency, which can strain manpower for the IT organization.
Now, here’s where a VPN wins. ZTNA might be the more secure choice for a company as a whole, but a VPN has so much to offer for both the organization and the individual.
A VPN cloaks the users’ IP addresses, which anonymizes their internet approach. According to the server’s location, they’ll gain the ability to access geo-restricted content no matter where they are. This is a feature ZTNA lacks, which gives the VPN a boost in this comparison section.
The Best ZTNA Solutions
The new security model is growing in popularity among organizations and promises to change the cybersecurity landscape.
Following the Zero Trust principle and implementing the ZTNA technology are two different things. Just like VPNs, ZTNA can be implemented through several providers.
However, if ZTNA’s motto is “trust no one,” yours should be too as not all providers are to be trusted. But which service provider should you pick? Check the list below as we included the best ZTNA providers in 2022:
- Perimeter 81
- Twingate
- Okta Identity
- Ping Identity
- Symantec Secure Access Cloud
- Zscaler Private Access
- Google BeyondCorp
- GoodAccess
Most of these providers are budget-friendly. Of course, each one of them supports different features, comes with a set of “Pros and Cons,” and covers different organization sizes.
ZTNA – Organizational Security at Its Best
Zero Trust improves security and the user experience both on and off-premises. Cyber attacks are constantly increasing, especially on small or medium organizations.
ZTNA is the perfect example of a “Trust Noone” policy since even employees can pose a threat to a company. This has recently occurred with the OpenSea company.
Both ZTNA and VPNs are great ways for enhanced security. We can’t recommend one over the other as they both can benefit a company in a unique way. It all depends on what the company is looking for and what security measurements it needs to implement.





