Cacti and Realtek Vulnerabilities – Malware Bots Everywhere
Vulnerabilities are everywhere, especially those that can compromise systems, leading to malicious exploitations. Even the biggest tech companies, such as Apple, have fallen victim to security flaws. Now, two new vulnerabilities emerged, allowing cybercriminals to deploy ShellBot and Moobot malware.

Cacti and Realtek represent two major flaws that have been exploited by cybercriminals since January. Unfortunately, this is not the first time these two vulnerabilities have been in the spotlight.
A couple of months ago, other malware families were spreading due to these flaws. With ShellBot and Moobot around now, things are getting riskier every day. What’s up with these flaws? What can cybercriminals do if they exploit them? Here’s what we know.
ShellBot & Moobot Malware Families Emerge
Vulnerabilities are everywhere, and every company/system is susceptible, regardless of the implemented security measures.
A while ago, Adobe ColdFusion took the spotlight as the CVE-2023-26360 flaw allowed threat actors to achieve arbitrary code execution.
Now, threat actors are exploiting Cacti and Realtek vulnerabilities in campaigns that have been ongoing since January. What’s worse is that we’re in March, and there’s no indication that the campaigns have stopped.
According to a report published by Fortinet:
- CVE-2021-35394 (Realtek): An arbitrary command injection vulnerability that affects UDPServer due to insufficient legality detection on commands received from clients.
- CVE-2022-46169 (Cacti): A critical command injection flaw in the Cacti fault management monitoring tool.
Once threat actors successfully exploit these vulnerabilities, they can enlist the infected devices in DDoS (distributed denial of service) swarms.
The recent attack involves Moobot and Shellbot. However, the same vulnerabilities were targeted by different families in the past. Those include Fodcha, RedGoBot, Mirai, Gafgyt, and Mozi.
Moobot’s main job is to infect a device and further download a script containing its configuration. Once that is in place, it establishes a connection with the C2 server.
This particular malware can kill other bots present on the device. That way, it can ensure that it can harvest the maximum hardware power to initiate DDoS attacks.
As for Shellbot, this malware establishes communication with the C2 and awaits further commands such as the ones listed below:
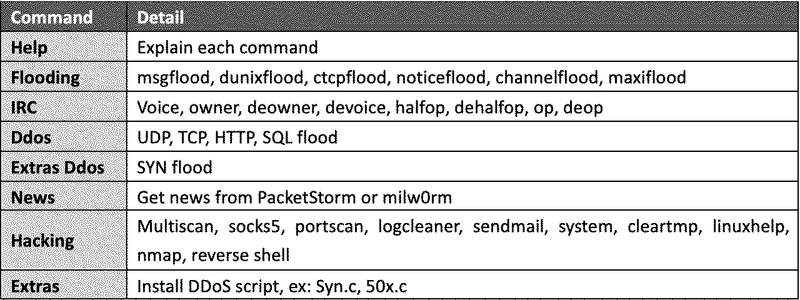
According to the Fortinet report, users should use strong admin passwords to defend against Mootbot and ShellBot.
Not only that, but they should also download and install the latest. security updates to omit any possibility of having these vulnerabilities.
Cacti and Realtek – Malicious Commands at Their Best
Devices age, and they might be abandoned by the vendor. If your platform is no longer supported by the vendor, you must replace it immediately.
If you don’t, you won’t receive the necessary updates to fix the present flaws. Always make sure that your device’s software is up-to-date. Don’t take this lightly – your online privacy and security are at risk.





