RomCom Hackers Strike – NATO Summit Attendees Targeted with Phishing Attacks
Using phishing tactics to target victims has become a common tactic among cybercriminals as of late. In fact, 2023 has seen its fair share of such attacks, impersonating big names such as WhatsApp, Gmail, Outlook, and the like. However, a recent attempt took a different route, as RomCom Hackers are using this particular tactic to target NATO Summit Attendees.

The NATO Summit is taking place in Vilnius, Lithuania, which presented a perfect opportunity for RomCom hackers to initiate their move against organizations supporting Ukraine and the summit’s guests.
This particular phishing campaign includes two very well-executed malicious documents that can easily lure victims. What is this attack all about? How are they executing their malicious activities? Here’s everything we know.
NATO Summit Under Attack – ROMCOM Hits Hard
Threat actors don’t just sit around relying on their current tools to target victims. Instead, they elevate their techniques regularly to match whatever security precaution a certain company/entity might have implemented.
In most cases, phishing attacks have shown to be very effective, as they trick individuals easily, courtesy of legit disguises that can fool anyone.
Speaking of disguise, in this particular campaign, ROMCOM hackers are impersonating the Ukranian World Congress organization, sending phishing emails with topics related to the NATO Summit.
They even created a website that looks exactly like the Ukrainian World Congress page hosted on a “.info” domain.
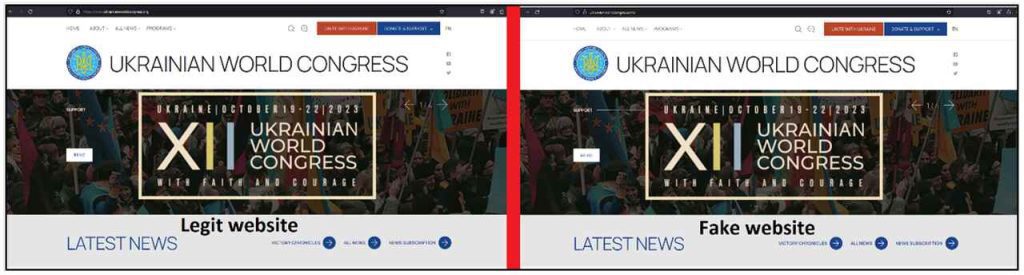
The image above clearly shows the resemblance between the two. However, it also shows the one difference that deems the hackers’ website “Fake.” The original one uses the “.org” top-level domain.
Unfortunately, most users don’t notice that, and they fall victim to such attacks with ease. As we stated above, the attack seems to have two malicious documents used to trick the attendees.


According to BlackBerry’s report, the users end up on the fake page as a result of a possible spear-phishing attack.
Once they download and launch the malicious documents, they would initiate an outbound connection. Sadly, it doesn’t stop here. Additional components find their way from the attacker’s command and control (C2) server.
These components directly target Follina (CVE-2022-30190) vulnerability, which easily allows the attacker to conduct a remote code execution (RCE)-based attack.
The NATO Summit is Under Attack
With full access to a victim’s device, ROMCOM can harvest very sensitive information, including username, network adapter info, and RAM size of the compromised computer.
That’s the best-case scenario. The worst would be the present backdoor that allows the threat actors to perform all kinds of malicious activities.
We’re talking about data exfiltration, injecting more payloads, deleting files or directories, and more. When it comes to phishing, you have a big part in stopping it.
Remain vigilant. Don’t believe anything you receive, and don’t click on any random link. You never know what’s waiting on the other end.




