Can You Have a Working Blockchain VPN?
‘Blockchain’ is a word of the day along with ‘privacy’ and ‘online security.’ Blockchain is a technology and method for decentralized storage and transfer of data between computing devices. In fact, many researchers hint at blockchain being the future backbone for a number of online services such as financial transactions or virtual private networks (VPN). But what is a Blockchain VPN? Can you have a working one? Find out in this comprehensive guide.
Blockchain VPN 101 – The Basics
A VPN acts as a secure tunnel for exchanging data, or messages, that encrypts data in transition. As a result, it makes it unusable for any man-in-the-middle such as your Internet service provider (ISP), a malicious actor such as a hacking group, or government agencies snooping online communications.
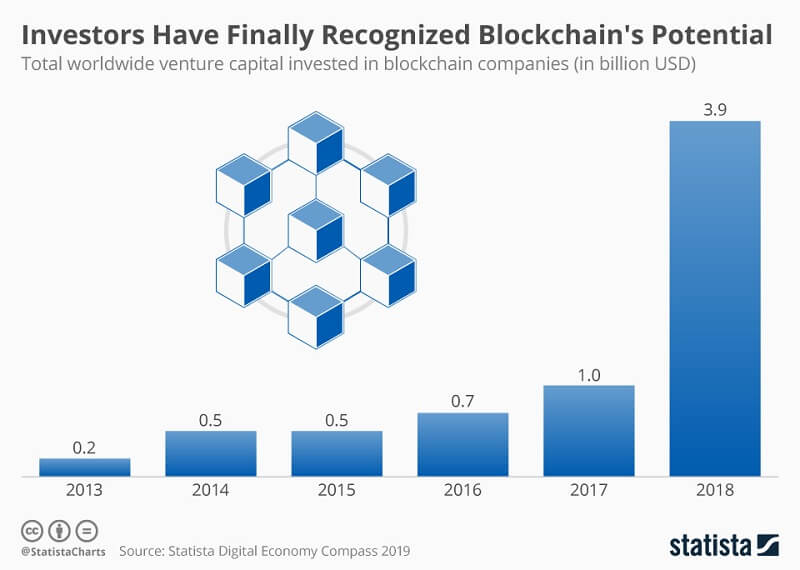
Users are finally waking up to how important the Blockchain technology really is. That includes top investors. Back in 2018, investment in blockchain companies skyrocketed to $4 billion, which shows how important it has become.
Source: Statista
You can use blockchain in the VPN context in two ways: First, you can utilize the VPN to make your connection to a blockchain network more private and secure. Second, you have at your disposal a decentralized, or blockchain-based, VPN service. There are such VPNs that already gained some popularity, reaching 100,000 users.
While it is possible to use current centralized VPN applications to add a further security layer to your online communications, the case with having a genuine blockchain VPN offers software developers a few challenges to solve.
How to Use Centralized VPN for Blockchain
Well, we all use a centralized VPN right now. What it means is that you use our VPN servers that belong to a centralized service provider. Each piece of data you exchange with other machines goes through this very VPN connection.
Blockchain, for its part, provides the foundation on which any digital currency, or cryptocurrency, is built on. Popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum exist on and in the blockchain. That’s where users create digital wallets to deposit and withdraw the respective cryptocurrency.
How Does it Protect Us?
 A blockchain network is a secure one as its decentralized technology stores your data and meta-data about your transactions, not on a single machine but on multiple computers that make the network.
A blockchain network is a secure one as its decentralized technology stores your data and meta-data about your transactions, not on a single machine but on multiple computers that make the network.
Virtually, no one can manipulate the stored data and claim that a single bit of anyone else’s data belongs to him.
This is good news. The bad news is that your connection to the blockchain network or digital wallet is as secure as any other connection.
Hence, you need tools such as a VPN to encrypt your online connections to the blockchain network and make sure that the virtual network safely obscures your real computer address.
So, you are using a VPN to secure your blockchain connections. However, a centralized VPN, such as the ones currently in use, sometimes poses a security risk themselves. Why? A single compromised VPN server within a centralized system enables bad actors to steal data such as your login credentials.
The same applies to vulnerable VPN software. Hence, your connection to a blockchain network using a VPN is as secure as your connection to any other network.
Blockchain ensures no one can claim your digital data, such as cryptocurrency or intellectual property. But it has its limits. It does not protect against someone using your login credentials to access and operate with this data. In this scenario, you might want to use a decentralized VPN service.
Using Decentralized Blockchain VPN
A decentralized blockchain-based VPN network is exactly what its name suggests. It operates in the same fashion as any other decentralized ledger by not having a central control point and storing data on multiple machines while using these multiple machines to transmit data through a fragmented connection.
Effectively, each machine within such a system is acting as a VPN server, which in turn means that you need to hack each and every single node to hack the whole system.
It might be possible in theory. However, it is beyond the reach of current technology in possession of both hackers and governments when you take into account that such a network comprises hundreds and thousands of computers each of which has some sort of protection be it a basic one.
Briefly speaking, a decentralized VPN starts with one VPN server and then offers incentives to other servers i.e., nodes or individual machines, to offer VPN server services by sharing their bandwidth with users.
This method creates numerous potential exit points for any user connecting to the decentralized VPN service. This is in theory. Let’s have a look at what we have in reality at this stage.
Challenges before Blockchain VPNs
In short, there is no genuine blockchain-based VPN at this very moment. All decentralized VPN services still have centralized server locations, while most of the security protocol and exchange services originate from a managed server location.
Thus, these are VPN services that are making only the first step toward blockchain-based VPNs. In other words, they’re still not truly decentralized services i.e., blockchain services.
One of the problems is that while the ‘original’ VPN server might offer secure standards for tunneling and encryption, each individual node offers a varied level of service in terms of available bandwidth and speeds. How you balance the loads within such a network is another open question.
Then, you face the problem with the security of logging to an individual node across the network before you have a critical mass of networked nods that make it impossible to reassemble a logging or control request even in case of someone being able to decrypt your encrypting algorithms.
As a matter of fact, you will have a ‘blockchain’ VPN only after reaching Stage 3. It is where you have the critical mass of independent nodes, or machines, that effectively build a blockchain network.
Prior to that, any VPN service will work largely like any other P2P network. It only offers more freedom to individual nodes to operate within a larger centralized network.
Concluding Words
We noted that ‘blockchain’ is a buzzword. We also looked at the figures showing how investment in blockchain companies skyrocketed.
The wave of blockchain investments covers any industry imaginable, and no online business niche will remain untouched by the implementation of blockchain technologies.
But, what you should know is that we are far, far away from viable blockchain implementations in the field of VPN services. At this stage, the Ethereum blockchain appears as the most likely platform on which blockchain-based VPNs to flourish.
If this is to happen, though, major service providers should be convinced to adopt it and start earning cryptocurrency by sharing their bandwidths with the average user looking for a VPN service.
And, furthermore, the industry will have to withstand the pressure coming from governments that are looking for ways to control online communications.