From Malware to Ransomware – Ursnif is Back with an Upgrade
We always say that cybercriminals have been coming up with innovative ways to target their victims. As cybersecurity advances, so should the threat actors’ tools, and that’s exactly what went down with the Ursnif (Gozi) malware.

Security measurements are updated regularly to keep up with various malware families. And now, Ursnif – one of the oldest and most successful forms of banking malware has resurfaced. Apparently, the malicious tool shifted to become a backdoor trojan that can be used for ransomware attacks.
The new variant – dubbed LDR4 has all the capabilities to outperform its previous versions. What can it do and how can it be used? Find out below.
Ursnif – A Malicious Transition
When it comes to malware, certain enhancements are always undergone to achieve higher success rates. For example, the BlackByte group has been around for quite some time now, wreaking havoc among big companies all over the world.
However, this particular group would’ve never achieved their malicious intent if they haven’t upgraded their form of attacks every now and then.
Ursnif has always been identified as a banking Trojan. However, as time went by, cybercriminals have elevated the malware’s capabilities, producing several variants (backdoors, spyware, file injectors, etc.) in the process.
In the past, particularly in 2020, Ursnif spread among users via phishing emails. The following image reflects an example where the malware masqueraded as a payment reminder.
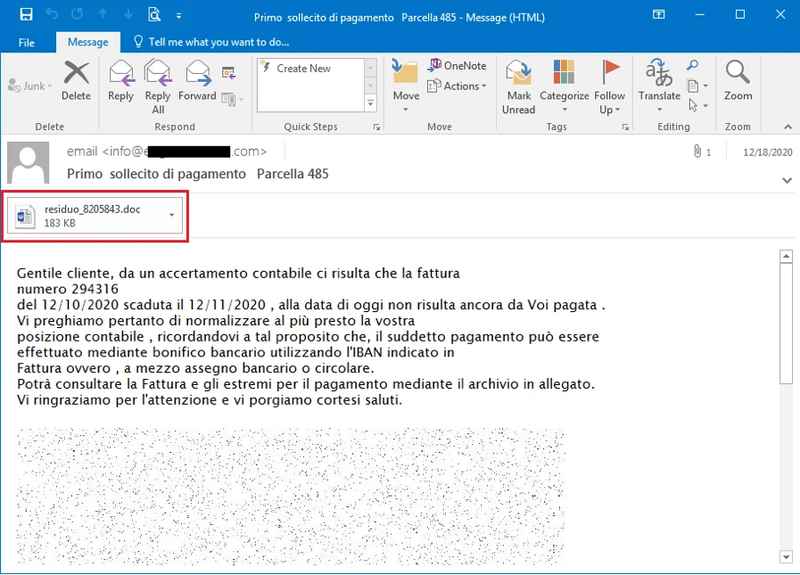
Now, this new variant goes by the name of LDR4 and it’s still using phishing emails to infiltrate the victims’ devices. Once the target executes Ursnif, it retrieves information about system services from Windows’ registry and then generates a user ID and a system ID.
As a result, the malware locates a list of commands to run on the host. LDR4 now boasts the following commands:
- Load a DLL module into the current process
- Retrieve the state of the cmd.exe reverse shell
- Start, restart, and stop the cmd.exe reverse shell
- Run arbitrary code
- Terminate
While most of these capabilities are not new, the operators behind the malware have made improvements to its code, allowing it to do more specific tasks such as being used for ransomware attacks.
Falling victim to Ursnif is far from inevitable. Since it uses phishing campaigns, all the organizations should do is avoid clicking on any link that might seem suspicious.
Gozi – One Heck of a Potentially Dangerous Malware
Gozi/Ursnif/LDR4, whatever you want to call it, is a very dangerous malware that apparently has been developing some new skills. Unfortunately, it seems like cyber criminals have invested a lot in upgrading it to reach such a status.
The malware can be used for ransomware attacks, which is quite alarming considering the rise of these types of malicious practices lately.




